A search engine is a software system and coordinated set of programs designed to search, retrieve and organize information from the vast content available on the World Wide Web.
Users enter a query through a web browser or mobile application and the search engine uses algorithms to index and rank relevant web pages, presenting results as a list of hyperlinks along with summaries, images, videos, or news.
Popular search engines such as Google, Bing and Yahoo help users quickly access information by matching queries with the most relevant content in their databases.
What are the components of Search Engine?
A search engine is built using three main components that work together to deliver search results: the web crawler, the database and the search interface.
- Web Crawler: A web crawler is an automated software program, also called a bot or spider, that scans and explores web pages across the World Wide Web to collect information.
- Database: All the information collected by the web crawler is processed and stored in a database, where it is organized for fast retrieval.
- Search Interface: The search interface is the user facing part of the search engine that allows users to enter queries and access relevant information from the database.
How does Search Engine works?
Search engines are generally work on three parts that are Crawling, Indexing and Ranking.
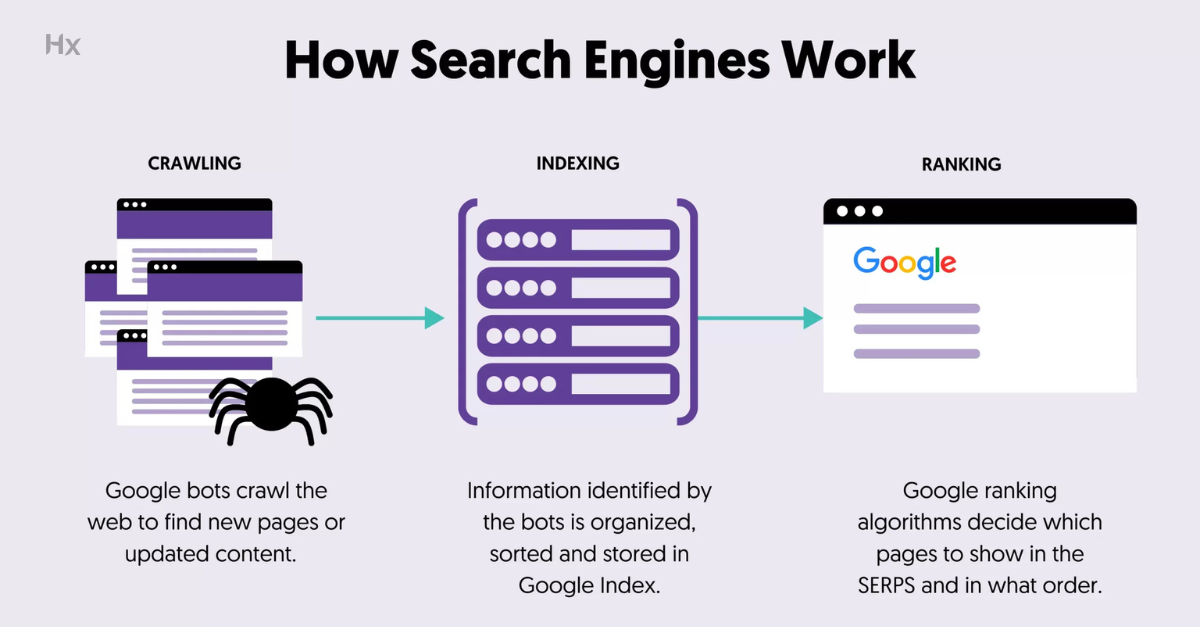
Crawling
Crawling is the process through which search engines discover web pages on the internet. Automated programs called web crawlers, spiders, or bots move from one website to another by following links. Before accessing a website, crawlers check the robots.txt file to identify which pages are allowed or restricted.
They analyze various elements of a page such as HTML structure, titles, headings, content, metadata, JavaScript and CSS. Since the web is extremely large and constantly changing, search engines use crawl policies to decide how often and how deeply a website should be crawled.
Some websites are crawled completely, while others are crawled partially based on factors like site size, authority and update frequency.
Indexing
Indexing is the stage where information collected during crawling is processed, organized and stored in a structured database called the search index. Search engines extract and save key details such as page titles, descriptions, keywords, content type, internal and external links and other ranking signals.
During this process, duplicate pages are identified and filtered and additional attributes such as geographical relevance and page usability are assigned. Indexing is essential because only pages stored in the search engine’s index are eligible to appear in search results.
Ranking
Ranking occurs when a user enters a search query into a search engine. The search engine searches its index to find pages that best match the query and then orders them based on relevance.
Specialized content search engines focus on specific segments of the web and selectively crawl and index only relevant content. For example, Creative Commons Search is designed to find content that is explicitly licensed for reuse under Creative Commons, limiting its search to that particular type of material.
Ranking algorithms evaluate multiple factors, including keyword relevance, content quality, backlinks, page authority and user experience.
Google and other search engines continuously update their algorithms to deliver the most accurate and useful results, displaying the most relevant pages on the Search Engine Results Page (SERP).
How do search engines work in response to a user query?
Ranking refers to the position at which a website appears on a search engine results page (SERP). Search engines determine rankings through a structured process that involves three main steps.
Step 1: Analyzing the User Query
In this step, the search engine identifies the user’s search intent by analyzing the query and breaking it into meaningful keywords. Keywords help the search engine understand what type of information the user is looking for. For example, a search query like “how to make a chocolate cupcake” signals a need for recipes and step by step instructions. Search engines can also recognize similar meanings in different phrases, such as “how to change a light bulb” and “how to replace a light bulb,” and are capable of interpreting spelling mistakes.
Step 2: Finding Matching Pages
After understanding the query, the search engine scans its index to find pages that best match the user’s intent. The type of results returned depends on the query. For instance, searching for “dark wallpaper” will primarily show image based results rather than text content.
Step 3: Presenting Results to the User
Finally, the search engine displays the most relevant results on the search engine results page. Typically, this includes organic listings along with additional elements such as paid advertisements, featured snippets, images and direct answers, depending on the nature of the search query.
How Search Engine makes Ranking Results ?
Not all search engines rank content in the same way, but many follow similar ranking principles. Google and other modern search engines evaluate and rank search results based on multiple factors to deliver the most relevant and useful information to users.
Query Meaning:
Search engines analyze the user’s query to understand search intent the exact type of information the user is seeking. This is done using advanced language models that interpret the meaning of words, context and user intent rather than just matching exact terms.
Relevance:
Search engines match keywords from the user’s query with keywords found in web content. Content that contains relevant keywords in important locations, such as titles, headings and body text, is considered more relevant.
Quality:
Content quality is measured through signals of expertise, authority and trustworthiness. Pages that receive backlinks from reputable and authoritative websites are generally considered more reliable and are ranked higher.
Usability:
Search engines assess how user friendly a webpage is, including factors like accessibility, page speed and mobile friendliness. Pages that offer a better overall user experience are more likely to rank well.
User Data:
User specific signals such as search history, location and personal settings can influence ranking results, allowing search engines to deliver more personalized outcomes.
In addition, search engines may use performance metrics like bounce rate and time spent on a page to refine rankings. Results may also vary depending on the search format, such as text based searches versus image or video searches.
Country specific search engines often give higher priority to websites published in the native language of the region rather than English-language sites. In addition, individual organizations, such as large corporations, may use customized search engines to index and retrieve content exclusively from their own websites. Many major search engine providers license or offer their search technologies for use on individual sites.
What are the goal of Search Engine ?
The main purpose of a search engine is to help users find accurate and relevant information quickly. Search engines evaluate content based on factors such as quality, relevance, and reliability to deliver the most useful results to users.
Business and Data Objectives
In addition to serving users, search engines support website owners and businesses by driving traffic, generating revenue and collecting user interaction data such as clickstream behavior. These objectives depend on maintaining user confidence in the accuracy and usefulness of the information shown on the Search Engine Results Page (SERP).
Importance of User Trust
User trust is essential for search engines to succeed. Users must feel confident that the information presented meets their needs and accurately answers their queries. Trust is built through transparent ranking practices and reliable content delivery.
Organic Results
Unpaid organic search results are generally perceived as more credible than paid advertisements, as they are ranked based on relevance and quality rather than promotional placement.
Authority and Credibility
Search engines like Google assess the authority of webpages to identify reliable sources of information. Pages with strong expertise, reputable backlinks, and trustworthy content are more likely to rank higher.
Privacy and User Protection
Privacy also plays a key role in building trust. Search engines such as DuckDuckGo emphasize user privacy by limiting data tracking and avoiding personalized filtering, which helps prevent biased or restricted search results.
How Does Search Engine Personalized results?
Search engines personalize results by creating digital user profiles based on collected user data. This data is gathered from the device or application used to access the search engine and helps tailor search results and advertisements to individual preferences.
Types of User Data Collected
Search engines may collect various types of user information, including search history, date and time of searches, location data, audio inputs, user IDs, device identifiers, IP addresses, device diagnostic information, contact lists, and purchase history. This data allows search engines to better understand user behavior and intent.
Role of Cookies
Cookies are small text files stored in a user’s web browser by websites they visit. Search engines use cookies to track browsing activity, remember user preferences, and personalize search results and ads. Cookies help retain settings such as language preferences, saved passwords, content filters, the number of results displayed per page, and session-related information.
Private and Incognito Browsing
Private or incognito browsing modes limit tracking only at the device level. During these sessions, search history and related data are not saved and are deleted once the session ends. However, these modes do not provide complete anonymity, as internet service providers, employers, and website domain owners can still monitor certain digital activities during searches.
Top 10 Popular Search Engines :
| No. | Search Engine | Key Specifications / Features |
| 1 | Most widely used search engine; advanced algorithms, AI-driven ranking, fast results, strong personalization, supports text, image, video, news, and voice search | |
| 2 | Bing | Microsoft’s search engine; strong image and video search, integrates with Windows and Edge, rewards users through Microsoft Rewards |
| 3 | Yahoo | Uses Bing’s search technology; offers integrated services like mail, news, finance, and sports |
| 4 | DuckDuckGo | Privacy-focused search engine; does not track users or store personal data; provides unbiased search results |
| 5 | Baidu | Leading search engine in China; optimized for Chinese language and local content; strong AI capabilities |
| 6 | Yandex | Popular in Russia and Eastern Europe; strong local search features; advanced image and map services |
| 7 | Ask.com | Focuses on question-and-answer style searches; returns direct answers along with traditional results |
| 8 | Naver | Leading search engine in South Korea; combines search with blogs, news, Q&A, and shopping content |
| 9 | Ecosia | Eco-friendly search engine; uses ad revenue to plant trees; powered by Bing search results |
| 10 | AOL Search | Uses Bing’s search technology; integrates with AOL’s news, email, and media services |
How does Search Engine Makes Money ?
Search engines make money in several ways, including the following:
Pay Per Click (PPC) Advertising
Search engines earn a significant portion of their revenue through pay-per-click advertising. Advertisers place ads on search engine results pages (SERPs) or within website content, and they pay each time a user clicks on their advertisement. Highly searched keywords usually cost more due to increased competition.
User Data Monetization
Search engines collect user data such as search history, location details, and browsing behavior. This information is used to create digital user profiles, enabling search engines to deliver targeted advertisements and increase advertising effectiveness.
Contextual Advertising
Contextual ads are displayed based on the user’s current search query or browsing activity. For example, when a user searches for a product, related ads may appear alongside the results or in shopping sections, improving relevance and user engagement.
Donation Based Revenue
Some search engines operate with a social mission and use their platforms to support nonprofit organizations. They may donate a portion of their advertising revenue or provide tools to help raise funds for charitable causes.
Affiliate Marketing
Search engines also generate income through affiliate partnerships. In this model, the search engine earns a commission when users click on affiliate links and complete a purchase or specific action on a partner’s website.
The future of search engines:
The future of search engines will focus on AI driven personalization, voice and visual search, improved user intent understanding, enhanced privacy protection and real time results. Search engines will deliver more accurate, context aware and conversational responses while balancing relevance, trust and user data security.
Pingback: Google Business Profile Updates | GMB SEO Guide
Pingback: What Is SEO? Meaning, Goals & How It Works in 2025