This introductory guide explores what SEO is and how it works in 2025. As technology continues to evolve, websites and the way they are built, optimized and accessed are constantly changing. The devices people use to search have expanded and so have search behaviors.
Today, searches can be voice activated, clicks may happen as taps on mobile screens and search results themselves are increasingly shaped or summarized by artificial intelligence (AI).
This guide breaks down these evolving aspects of SEO and provides practical insights and resources to support your continued learning and success.
What is SEO:
SEO (Search Engine Optimization) is the practice of improving a website’s visibility in search engines like Google by optimizing its content, structure, and technical performance without relying on paid ads.
It helps search engines understand your website and connect it with users by delivering relevant, valuable results based on their search queries.
By aligning with search engine algorithms through keyword research, quality content, technical optimization, and authority building, SEO increases organic traffic, relevance, and trust ensuring your website attracts the right audience, not just more visitors.
Goal Of SEO:
The goal of SEO is to secure first page visibility on search engine results pages (SERPs) for the most relevant and high value keywords, driving qualified content to the user query.
More specifically, SEO aims to:
- Help search engines understand your content and rank it for relevant search queries
- Drive high quality, organic traffic to your website without paid ads
- Improve user experience through faster load times, clear structure, and valuable content
- Increase credibility and authority by building trust with search engines and users
- Support business outcomes such as leads, conversions, sales, or brand awareness
In short, the goal of SEO is not just more traffic, but more relevant traffic that converts.
The greater your visibility in search results, the more likely users are to discover, visit, and engage with your website.
How Is SEO Different from SEM and PPC?
SEO, SEM and PPC are closely related terms you’ll often encounter in search marketing discussions. Understanding how they differ and how they work together helps clarify where each fits within a digital marketing strategy.
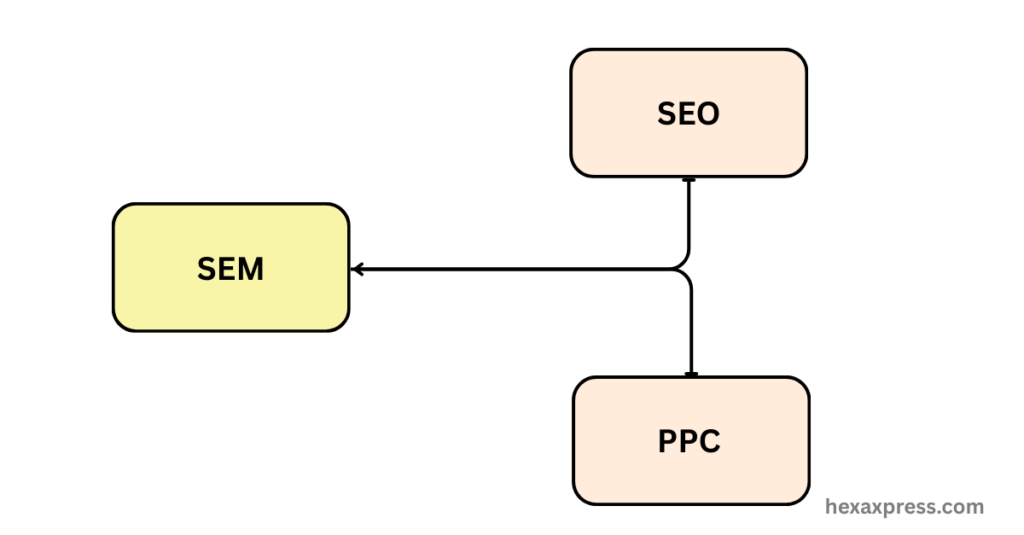
SEO vs. SEM
SEM stands for Search Engine Marketing, commonly referred to as search marketing. It is an umbrella term that includes all strategies used to drive traffic from search engines, both organic and paid.
- SEO (Search Engine Optimization) focuses on earning traffic from organic (unpaid) search results.
- PPC (Pay-Per-Click) focuses on generating traffic through paid search ads.
- SEM includes both SEO and PPC.
Think of SEM as a coin:
- One side represents SEO (organic search).
- The other side represents PPC (paid search).
SEO vs. PPC
PPC (Pay-Per-Click) is a form of digital advertising where advertisers pay each time a user clicks on their ad. Advertisers bid on keywords they want their ads to appear for, and when users search those terms, the paid ads appear at the top of search engine results pages.
The key difference between SEO and PPC lies in how traffic is earned:
- With PPC, you pay for each click on your ad.
- With SEO, clicks are earned organically although achieving strong rankings requires time, expertise, and ongoing investment, so organic search is not entirely “free.”
SEO and PPC: Complementary Channels
Rather than competing, SEO and PPC work best together. While PPC can deliver immediate visibility and traffic, SEO builds long-term authority and sustainable growth. When budget allows, combining both channels often produces the strongest return on investment (ROI).
How We Use These Terms
In the search marketing industry, the terms SEM and PPC are sometimes used interchangeably. However, in this context:
- SEM refers to the combined use of SEO (organic search) and PPC (paid search).
- PPC refers specifically to paid search advertising.
Understanding these distinctions helps you build a more balanced and effective search marketing strategy.
Why Is SEO Important?
SEO is one of the most critical digital marketing channels for sustainable growth.
Organic search accounts for over half of all website traffic, with studies showing that
- approximately 53% of visits originate from unpaid search results.
- With more than 8.5 billion searches performed on Google every day
- Google commanding about 91% of the global search engine market,SEO plays a vital role in helping businesses stay visible, competitive, and discoverable online.
Here’s a polished, clear, and professional rewrite that improves flow, removes repetition, and keeps the original meaning intact while sounding more authoritative and marketing-ready:
Trillions of searches are performed every year and for most websites, search remains the primary source of traffic. This makes it essential for brands and businesses to be “search engine friendly” across every platform where users can discover them.
Improving your visibility and ranking higher than competitors in search results directly impacts your bottom line driving more traffic, leads and revenue.
SERP Features:
SEO is especially critical because today’s search engine results pages (SERPs) are highly competitive. They are no longer made up of just blue links, but are packed with advanced features and paid placements, including:
- AI Overviews
- Knowledge panels
- Featured snippets
- Maps
- Images
- Videos
- Top stories (news)
- People Also Ask
- Carousels
Another key reason SEO matters is sustainability. When paid advertising stops, so does the traffic. Social media traffic is often unpredictable and significantly less reliable than it once was. In contrast, strong SEO continues to deliver value over time.
SEO is the foundation of holistic marketing. Once you understand what your users are searching for and how they behave, that insight can be applied across your entire digital presence, including:
- Paid and organic campaigns
- Website content
- Social media platforms
Organic search drives high intent traffic that supports core business goals such as conversions, visits and sales. It also builds trust,websites that rank well are typically seen as more authoritative and credible, qualities that search engines like Google actively reward.
Types of SEO and Specializations
Think of SEO like a sports team. To win, you need a strong offense, a solid defense, and an engaged fanbase.
- Technical SEO (Defense): Optimizing the technical foundation of your website to ensure search engines can crawl, index, and rank it efficiently.
- On-site SEO (Offense): Optimizing website content to meet user intent and improve relevance, engagement, and rankings.
- Off-site SEO (Fanbase): Building brand signals and authority through external efforts such as brand assets, reputation building, and demand generation to strengthen trust, expertise, and recognition.
You have full control over technical and on site optimizations. While off site SEO is less controllable,since it depends on third party platforms and external signals,it remains a critical part of this three pillar SEO strategy. Together, these elements form a balanced and sustainable approach to long term search success.
SEO Specialties
Search engine optimization includes several specialized disciplines, each with its own strategies, challenges, and technical requirements. These SEO specialties go beyond traditional SEO, often demanding advanced tactics and deeper expertise.
Five key SEO specialties include:
Ecommerce SEO
Focuses on optimizing large-scale online stores by enhancing category and product pages, faceted navigation, internal linking, product imagery, customer reviews, structured data (schema), and overall site architecture to drive visibility and conversions.
Enterprise SEO
Involves managing SEO at scale for large organizations, typically with websites containing millions of pages or brands generating significant annual revenue. Enterprise SEO requires navigating complex infrastructures, coordinating with multiple stakeholders, and managing longer development cycles for implementing SEO changes.
International SEO
Targets global and multilingual audiences by optimizing websites for multiple regions and languages. This includes handling hreflang implementations, localized content, and search engine optimization for international platforms such as Baidu, Naver, and others beyond Google.
Local SEO
Local SEO Aims to improve visibility in local organic search results by optimizing business listings, managing customer reviews, ensuring accurate location data, and strengthening local relevance signals across search platforms.
News SEO
Prioritizes speed and real time optimization to ensure content is indexed as quickly as possible. Success in News SEO requires expertise in Google Discover, Top Stories and Google News, along with best practices for structured data, paywalls, section pages and news specific technical requirements.
Video SEO:
Optimizing video content (YouTube, site videos) for search and video platforms.
Image SEO:
Optimizing images to rank in Google Images and other image search results.
Mobile SEO:
Ensuring excellent user experience and ranking on mobile devices, a crucial factor for Google.
International SEO:
Targeting multiple countries/languages with country specific or language specific strategies.
Content SEO:
A broad term focusing heavily on creating high quality, keyword rich content.
Ethical/Strategy Types
- White Hat SEO: Ethical, long term strategies that follow search engine guidelines (e.g., quality content, natural links).
- Black Hat SEO: Risky, forbidden tactics (e.g., keyword stuffing, link schemes) that risk penalties.
- Gray Hat SEO: Strategies that aren’t strictly white or black, operating in a risky middle ground.
Emerging Types
- AI SEO: Using artificial intelligence for optimization.
- Programmatic SEO: Generating large numbers of pages automatically for specific niches.
How SEO Works
SEO works by helping search engines understand your website and decide when to show it to users searching for related topics. The better search engines understand your content and trust your website, the higher you can rank in search results.
At a high level, SEO is a combination of people, processes, technology, and ongoing activities working together to improve visibility in search engines.
How Search Engines Find and Rank Websites
Search engines like Google follow a basic process to deliver results:
1. Crawling Search engines use bots (called crawlers) to discover new and updated pages by following links and reading sitemaps.
2. Rendering They process the page’s code (HTML, CSS, JavaScript) to understand how the page looks and functions.
3. Indexing The content and information from the page are stored in a massive database called an index. Only indexed pages can appear in search results.
4. Ranking When someone searches, search engines use algorithms to decide which pages are most relevant, useful, and trustworthy for that query.
Different platforms work differently. For example, Google focuses heavily on relevance and quality, YouTube prioritizes watch time and engagement, and marketplaces like Amazon emphasize product relevance and sales performance.
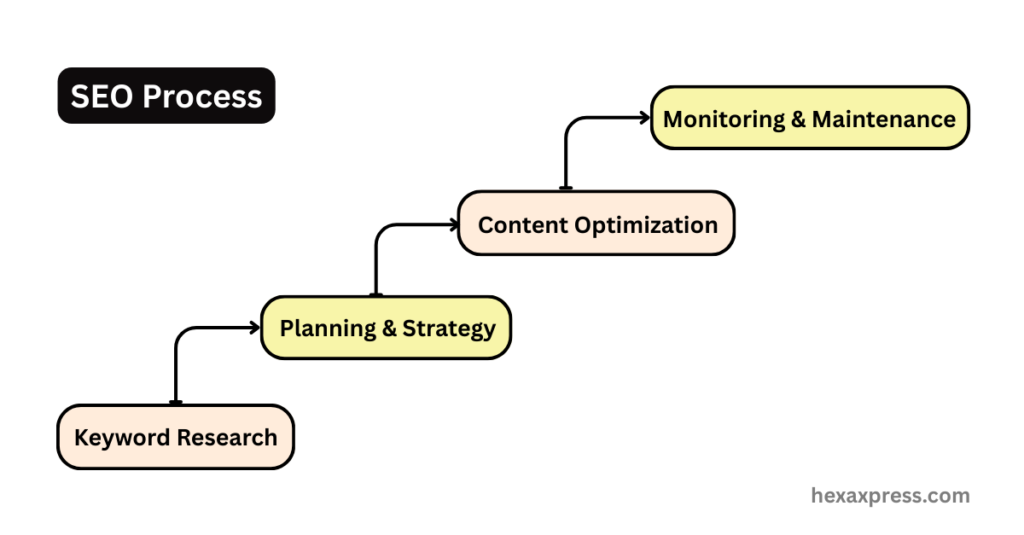
Research: The Foundation of SEO
Search Engine Optimization starts with research to understand users and competition:
- Audience research: Knowing who your audience is and what problems they want solved
- Keyword research: Finding the words and phrases people search for
- Competitor research: Understanding what competitors are doing well
- Website research: Identifying technical issues and content gaps
- Search intent analysis: Matching content to what users actually want (information, purchase, navigation, etc.)
Planning an SEO Strategy
An SEO strategy is a roadmap that defines goals and how to reach them. It includes:
- Setting clear goals and timelines
- Choosing the right metrics to measure success
- Aligning SEO with business objectives
- Selecting tools and resources
- Coordinating with content, marketing, and development teams
Creating and Optimizing Content
Once planning is complete, SEO moves into action:
- Creating helpful, relevant content
- Improving existing pages with better structure, keywords, and internal links
- Removing outdated or low-quality content that no longer adds value
Monitoring and Maintenance
Search Engine Optimization requires constant monitoring to catch issues early, such as:
- Traffic drops
- Broken pages or links
- Slow page speed
- Pages disappearing from search results
Regular checks help keep your site healthy and competitive.
Measuring and Improving Performance
SEO performance is tracked using tools like Google Analytics and Google Search Console. These tools help measure:
- Traffic growth
- Keyword rankings
- User behavior
- Conversions and engagement
Reports help identify what’s working, what’s not, and where improvements are needed.
SEO Is an Ongoing Process
SEO never truly ends. Search engines update algorithms, user behavior changes, competitors improve, and content becomes outdated. Continuous optimization is essential to maintain and grow visibility.
How SEO Evolves
SEO evolves alongside technology and society:
- Technology changes: AI powered search, mobile-first indexing, faster websites and better user experience
- Behavior changes: How people search on mobile devices, voice assistants and AI tools
- Social and economic changes: Shifts in consumer behavior, global events and market conditions
Because of this, SEO strategies must constantly adapt.
SEO as a Service and Career
SEO is both a marketing discipline and a professional service. Businesses invest heavily in SEO because search drives long-term, sustainable growth. As a career, SEO continues to grow, offering opportunities across technical, content, analytical, and strategic roles.